Flexibility in the copper comes from multiple factors. Of course the thinner the copper, the more flexible. In addition to the thickness (or thinness), copper grain also affects flexibility. There are two common types of copper that are used in the PCB and flex circuit markets. Electro Deposited (ED) and Rolled Annealed (RA).
Differences between Electrolysis Deposition Copper Foil and Roll Anneal Copper Foil
1. ED copper (Electrolysis Deposition Copper Foil)
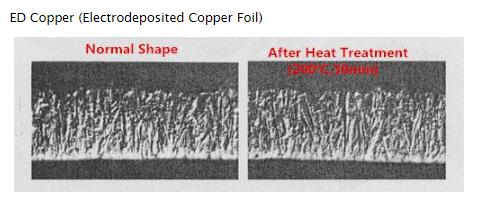
Formation: Melt copper into dilute sulfuric acid, it becomes bluestone solution.
Through a high electric field, copper attach on the metal drum. With the rolling of metal drum, thin copper foil finally formed.
Advantage: Low cost, ED copper has better conductivity than RA copper.
Shortage: Unsuitable for small lines; bad bending resistance.
2. RA copper (Roll Anneal Copper Foil)
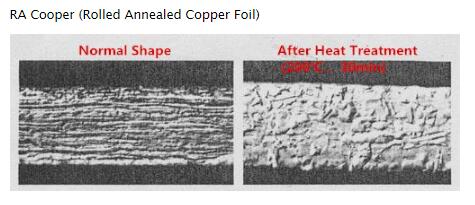
Formation: Roll copper block many times, and then do the annealing treatment with high temperature. The shape of its crystal is lamellar structure.
Advantage: Soft, smooth surface, suitable for flexible PCB and small lines.
Shortage: high cost
Because of different performances, RA copper and ED copper are used in different products which tend to different product requests. For example, the flex board needs to be bendable a lot, so obviously, RA copper will be a good choice. Otherwise, we could use ED copper with high electrical conductivity.
Whatever, you should select copper according to your circuits' requests (final board performance, cost, function...)




